In today’s digital landscape, securing remote access to systems is paramount. One effective method to enhance security is by configuring Remote Desktop Services (RDS) to limit the number of connections, thereby blocking access to the console session via Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to achieve this using Group Policy.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Open Group Policy Management Console (GPMC)
- Press Win + R, type gpmc.msc, and press Enter. (or locally run gpedit.msc)
- Navigate to the Specific Policy
- Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections.
- Configure the Policy
- Locate the policy named “Limit number of connections”.
- Double-click to open the policy settings.
- Enable and Set the Limit
- Select “Enabled”.
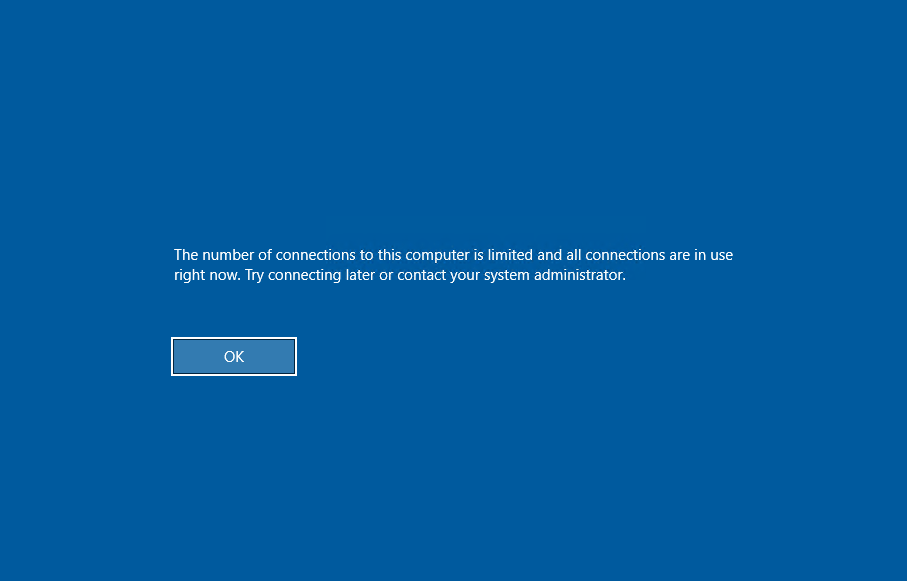
- In the “RD Maximum Connections allowed” box, set the desired number of connections. For instance, setting it to 1 ensures only one remote connection is allowed, effectively blocking access to the console session.
- Apply and Close
- Click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
- Update Group Policy
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run gpupdate /force and reboot the machine to apply the new policy settings.
Benefits of Limiting Connections
- Enhanced Security: Restricting the number of connections minimizes the risk of unauthorized access.
- Resource Management: Prevents system overload by limiting the number of active sessions.
- Control and Monitoring: Easier to monitor and manage remote sessions, ensuring compliance with security policies.
By following these steps, administrators can effectively block access to the console session using RDP, thereby enhancing the overall security of their systems. This simple yet powerful configuration helps maintain a secure and efficient remote access environment.