Task Manager is a handy utility that comes with Windows 11. It allows you to see how your system and apps are performing, and gives you the ability to manage them. You can use Task Manager to monitor your CPU, memory, disk, and network usage, view and end processes, start and stop services, and more.
To open Task Manager in Windows 11, you can use one of the following methods:
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc on your keyboard.
- Right-click the Start button and choose Task Manager from the menu.
- Type Task in the Start menu and click on Task Manager.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Del and choose Task Manager from the screen.
- Type taskmgr in any command prompt
In this blog post, I will share with you some of the best tips and tricks for using Task Manager in Windows 11. Let’s get started!
1. Find Out What’s Slowing Down Your PC
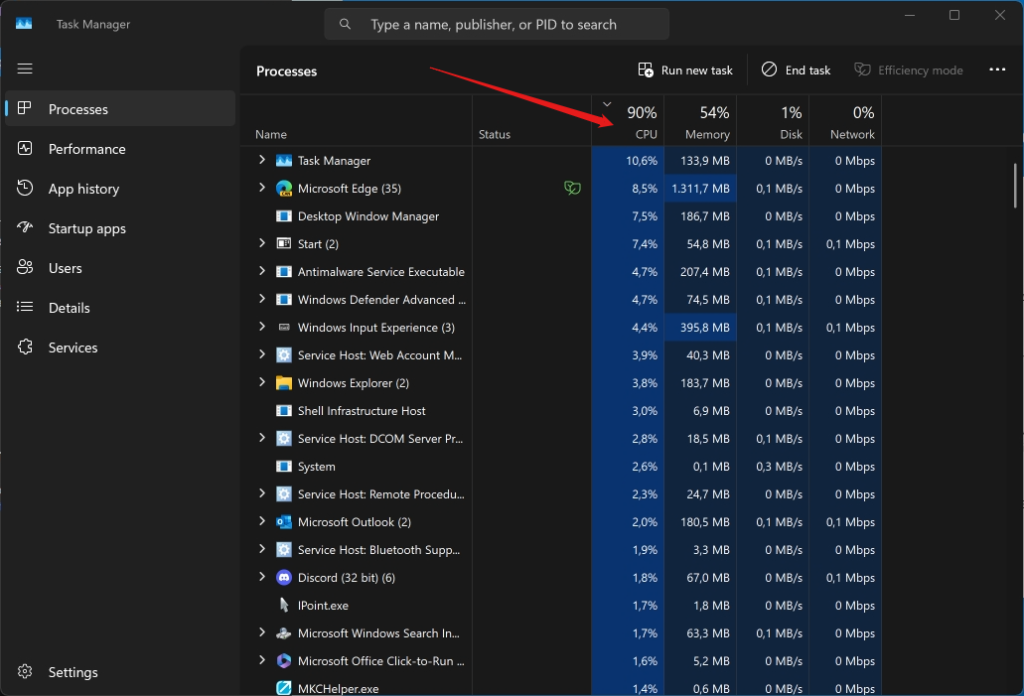
One of the most common uses for Task Manager is to find out what’s causing your PC to run slowly. To do this, you can sort the processes by CPU, memory, disk, or network usage, and see which ones are consuming the most resources. You can also add the GPU column to see how your graphics card is performing.
To sort the processes by a specific column, simply click on the column header. To add the GPU column, right-click on any column header and check the box next to GPU.
2. Shut Down Misbehaving Apps
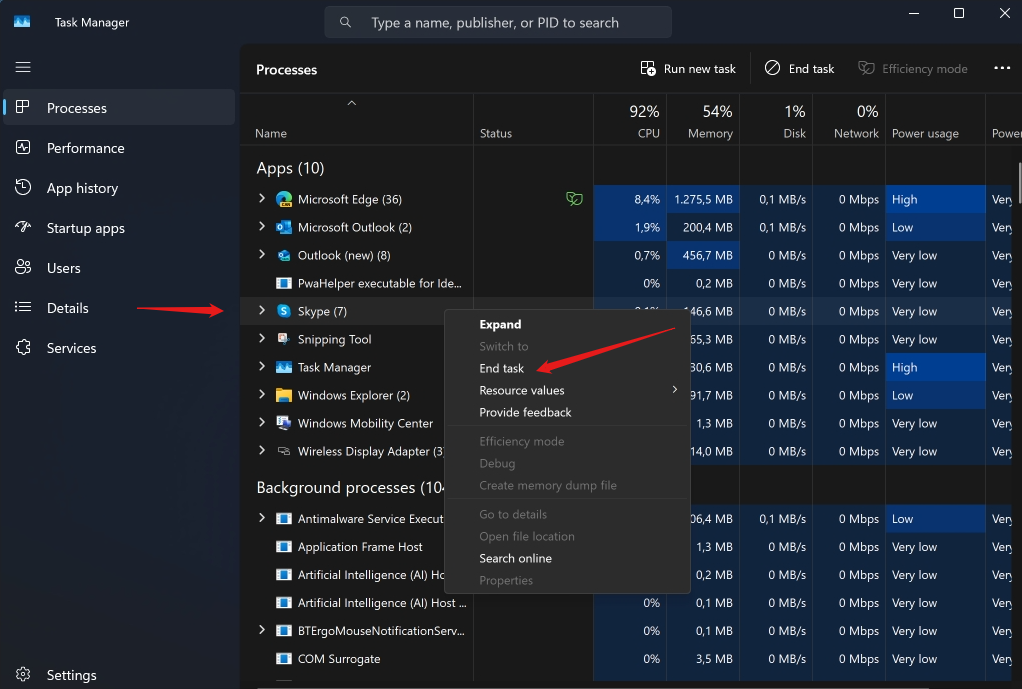
Sometimes, an app may stop responding or behave erratically, and you may not be able to close it normally. In that case, you can use Task Manager to force it to quit. To do this, select the app from the list of processes, and click on the End task button at the bottom right corner. Alternatively, you can right-click on the app and choose End task from the menu.
This will bypass any code in the app that prevents it from shutting down, and free up the resources it was using. However, be aware that you may lose any unsaved data or settings in the app.
3. Track Power Usage
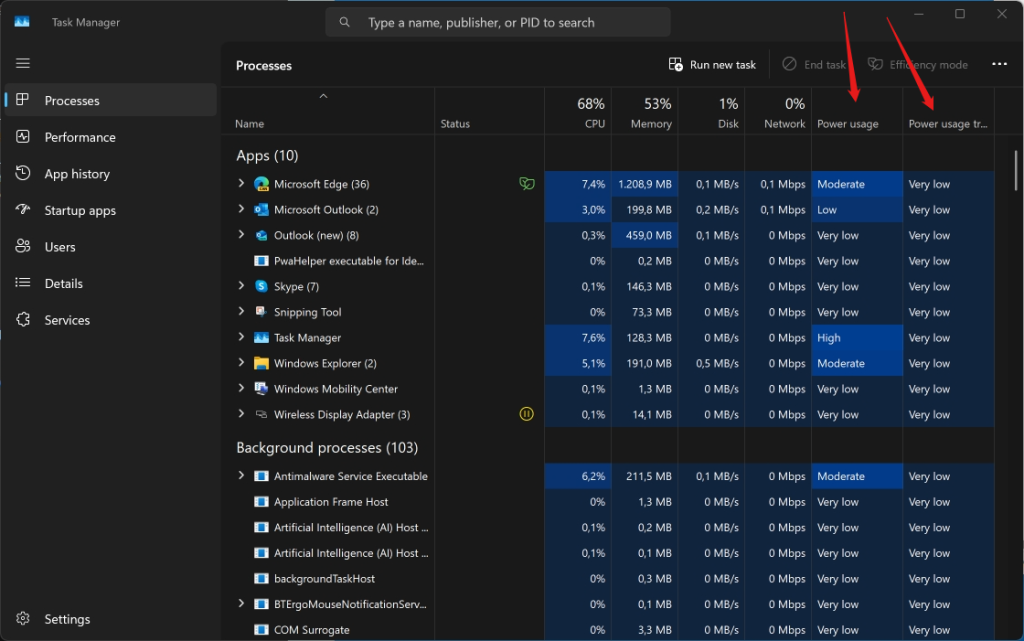
If you are using a laptop or tablet, you may want to keep an eye on your battery life and power consumption. Task Manager can help you with that, by showing you how much power each app is using. To see this information, you need to add the Power usage and Power usage trend columns to the processes tab.
To add these columns, right-click on any column header and check the boxes next to Power usage and Power usage trend. The Power usage column shows you the current power consumption of each app, while the Power usage trend column shows you the average power consumption over time. You can use this data to identify and close any apps that are draining your battery.
4. Add More Columns
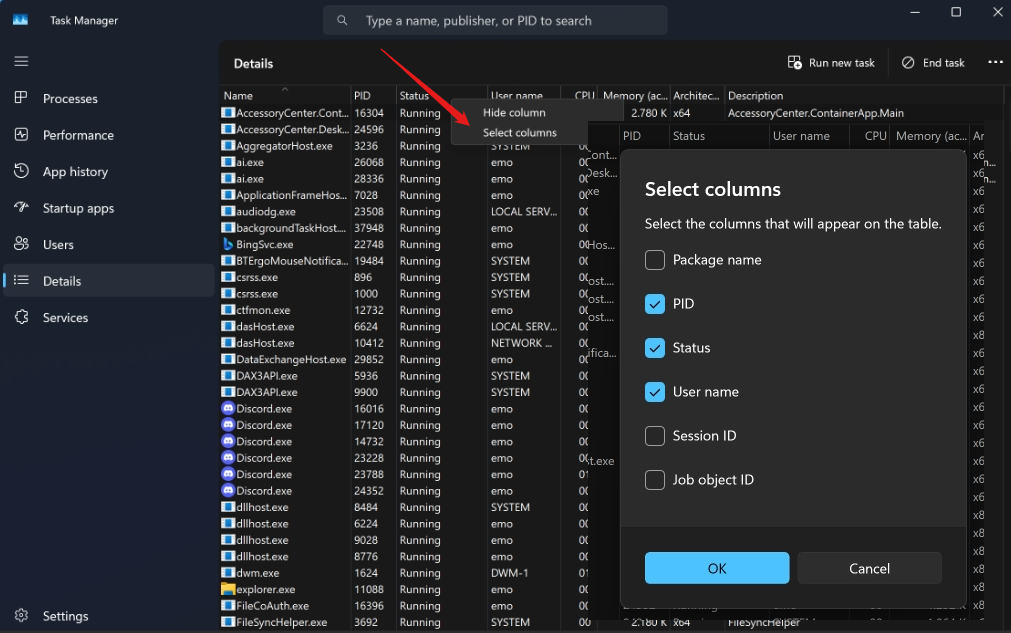
Task Manager has many more columns that you can add to the processes tab, depending on what information you want to see. For example, you can add columns for PID, command line, description, status, UWP context, and more. To add more columns, right-click on any column header and select hide column or show columns to check the boxes next to the columns you want to see.
You can also resize, reorder, and hide the columns by dragging them with your mouse. To reset the columns to their default settings, press Ctrl+Alt+Shift while opening Task Manager or use the reset option in settings.
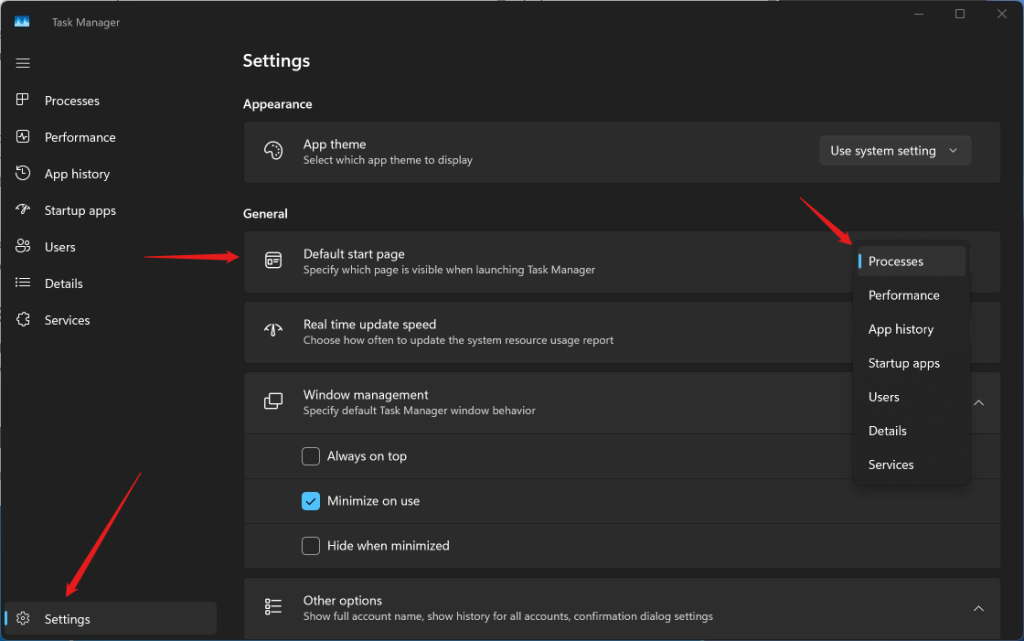
5. Change the Default Tab
By default, Task Manager opens with the processes tab, which shows you the list of running processes and their resource usage. However, you can change this setting and choose a different tab to open by default. For example, you may prefer to see the performance tab, which shows you the graphs of your system and app performance, or the app history tab, which shows you the historical data of your app usage.
To set a different page to appear when you launch Task Manager, open the settings menu at the bottom left of Task Manager and select Default Start Page. Then, pick the page you prefer from the dropdown menu.
6. Freeze the Task Manager Values
Sometimes, you may want to pause the Task Manager values and take a closer look at them, without them changing constantly. To do this, you can hold down Ctrl and it will pause until you let go of the button.
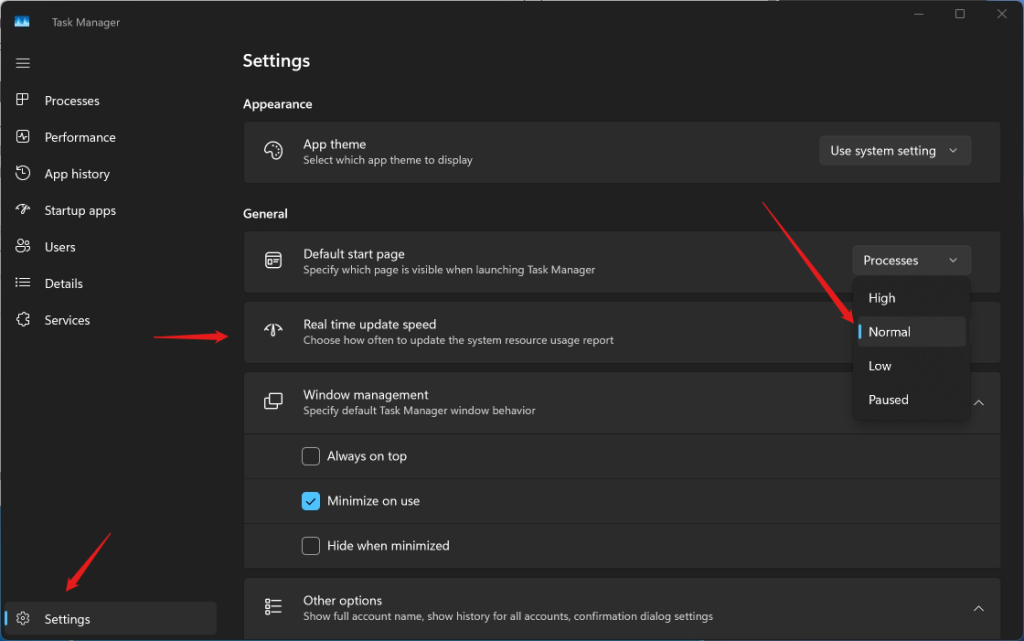
7. Change Task Manager Data Update Speed
By default, Task Manager updates the data every two seconds, which may be too fast or too slow for your needs. You can change this setting and choose a different update speed, from high to low. To do this, go to the view menu at the top of Task Manager, and click on Update speed. Then, choose the speed you want from the options.
I hope you found these tips and tricks useful, and learned something new about Task Manager in Windows 11. Task Manager is a powerful tool that can help you optimize your system and app performance, and troubleshoot any issues. I encourage you to try it out for yourself, and see what else you can do with it.
Do you have any other tips or tricks for using Task Manager? Do you have any questions or feedback? Let me know in the comments below. Thanks for reading!